Is used to convert the harmful VOC chemicals into harmless CO2 and water. Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO) is a very powerful air purification technology that has the ability to destroy particles as small as 0.001 microns.
Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive species that attack most of the organic molecules. They are highly oxidizing in nature which is attributed to their oxidation potential.
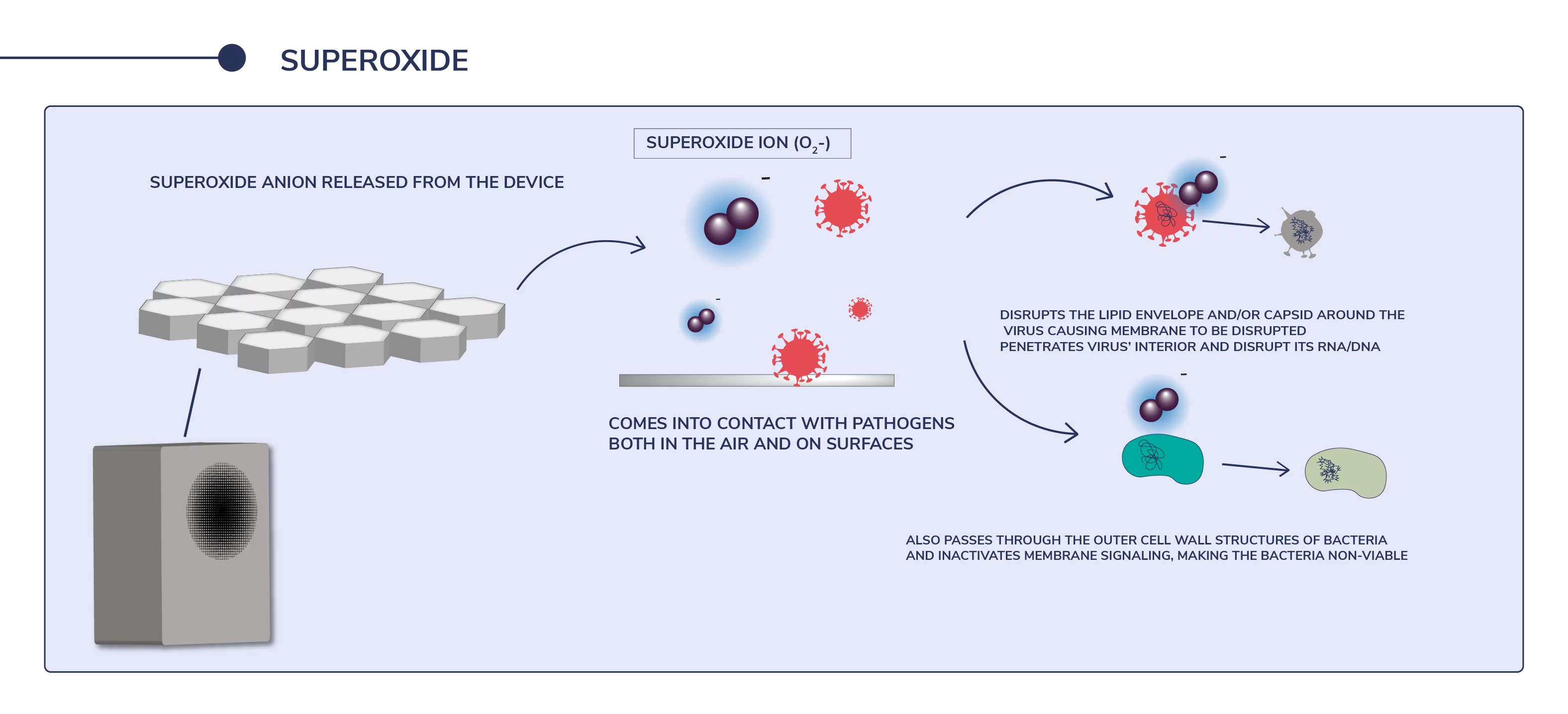
Disrupt the lipid envelope and/or capsid around the virus causing membrane to be disrupted.Penetrate virus’ interior and disrupt its RNA/DNA.Pass through the outer cell wall structures of bacteria and inactivate membrane signaling, making the bacteria non-viable.
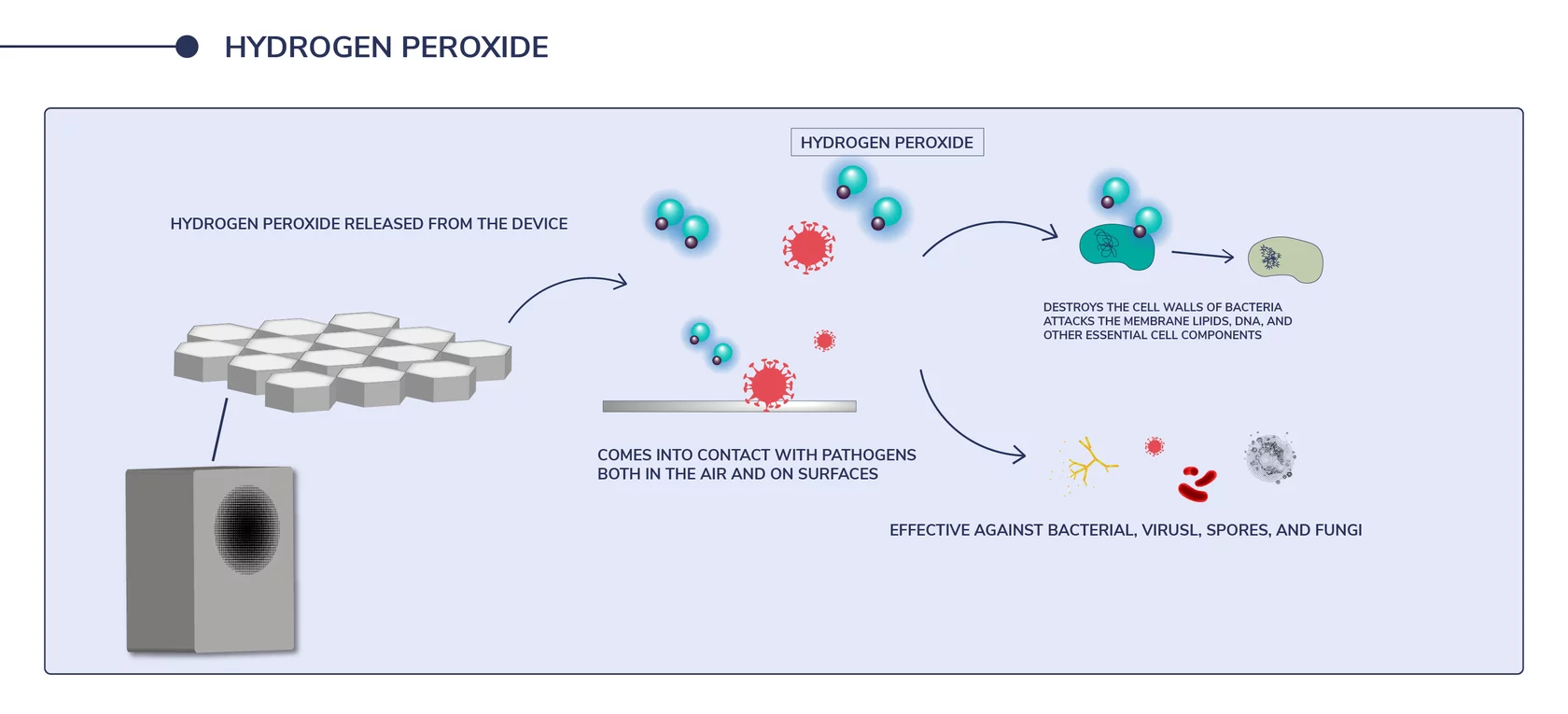
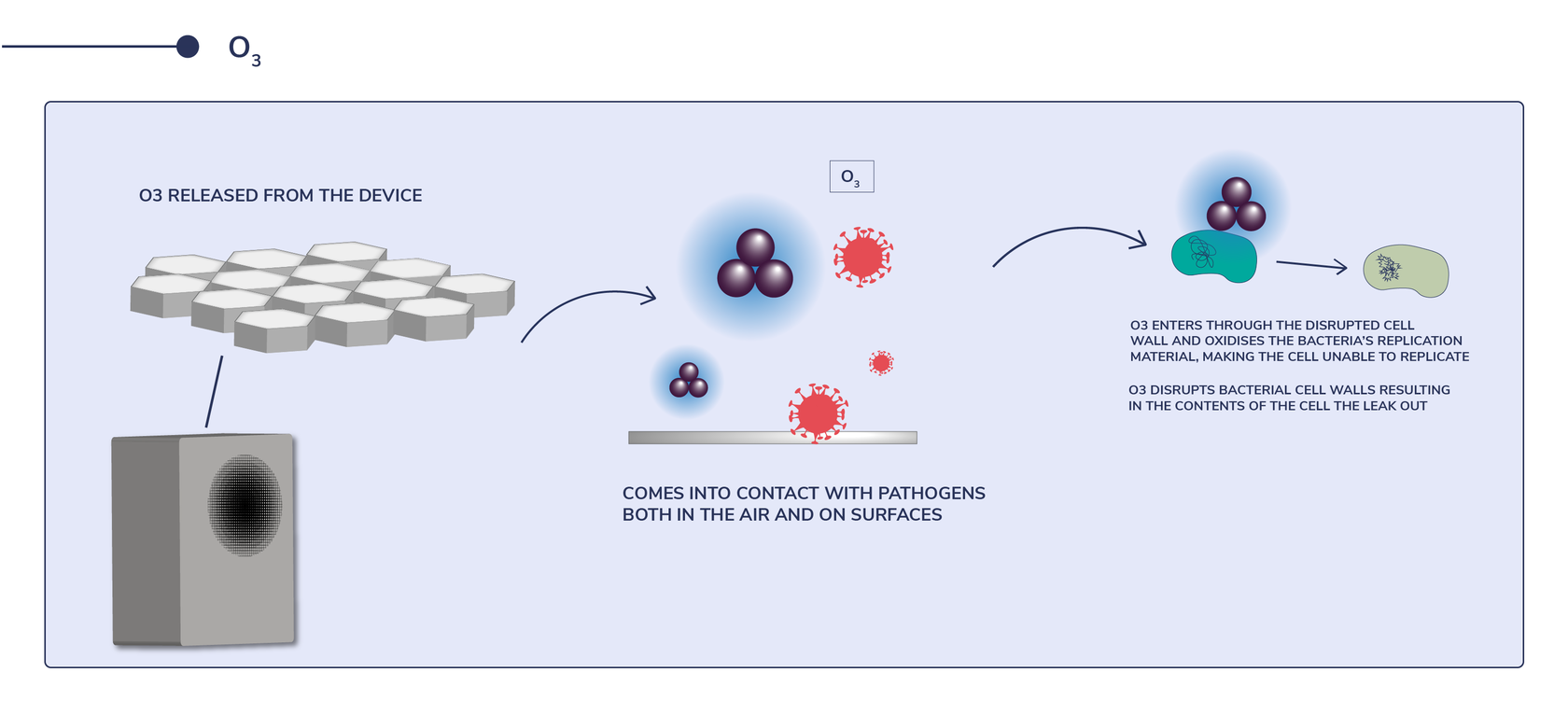
Come into contact with pathogens both in the air and on surfaces.Destroy the cell walls of bacteria Attacks the membrane lipids, DNA, and other essential cell components. Effective against bacterial, viruses, spores, and fungi.
Comes into contact with pathogens both in the air and on surfaces.Trioxygen enters through the disrupted cell wall and oxidizes the bacteria’s replication material, making the cell unable to replicate. Trioxygen disrupts bacterial cell walls resulting in the contents of the cell to leak out.
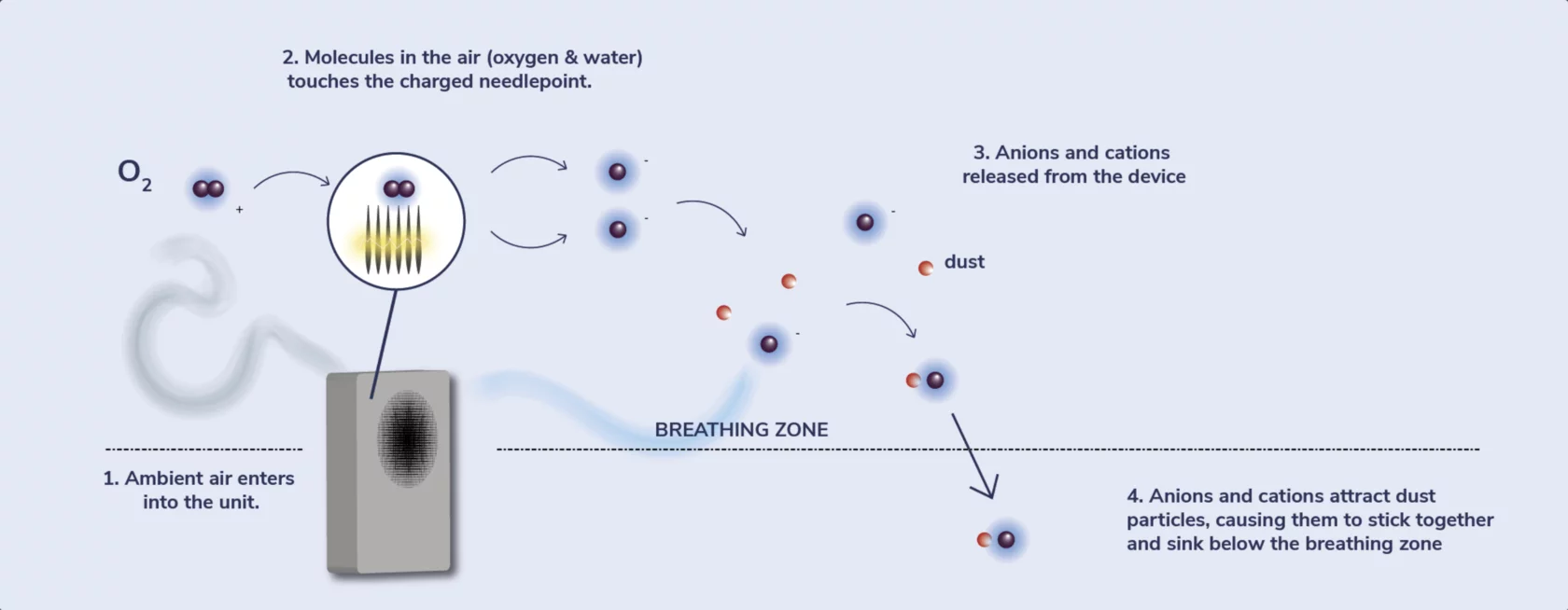
Negatively charged ions attach to dust particles flowing in the air and make them heavy enough to drop down from our breathing zone. Ions also disrupt outer membrane of the pathogen, causing the pathogen to be destroyed.
UVC light kills germs like viruses and bacteria through damaging molecules like nucleic acids and proteins. This makes the germ incapable of performing the processes that it needs to survive.
HEPA filter removes at least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and any airborne particles with a size of 0.3 microns (µm).
Activated charcoal works by adsorption, pollutants are trapped inside the pore structure of a carbon substrate.
Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO) is a very powerful air purification technology and has the ability to destroy particles as small as 0.001 microns. Photocatalytic oxidation destroys microbes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and chemically active compounds (CACs). The Photocatalytic Oxidation process combines UVC irradiation with a substance (catalyst) titanium dioxide (TiO2) which results in a reaction that changes malignant contaminants into water, carbon dioxide and detritus.
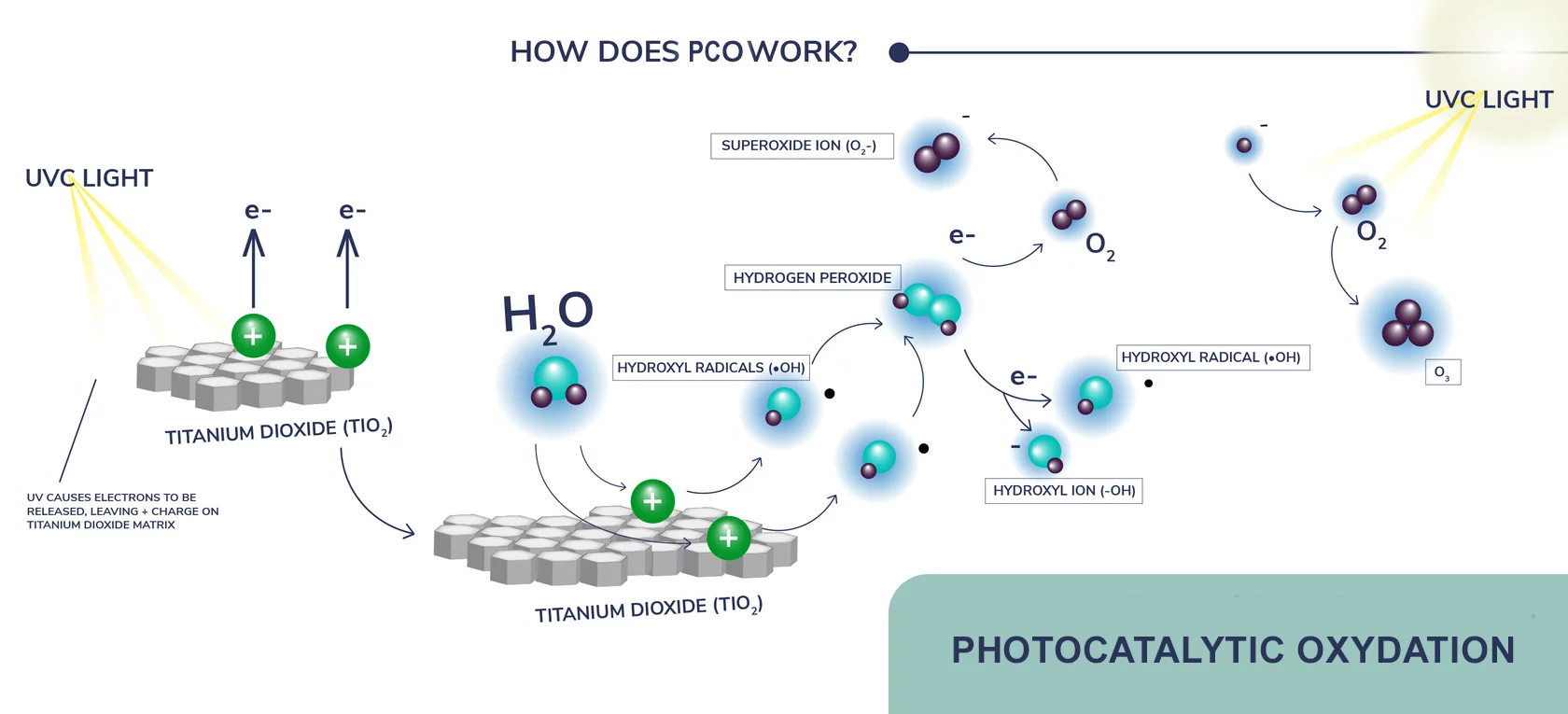
Hydroxyl radicals are photochemically formed in the atmosphere as a reaction to different wave lengths of light interacting with water and chemicals in the air. Hydroxyls are constantly being created in high quantities as a product of this natural process with each formation lasting less than a second. They instantly seek out and destroy contaminants in the air and on surfaces making them well known as ‘natures most powerful cleaning agent’. Hydroxyl radicals also contribute to the elimination of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane.
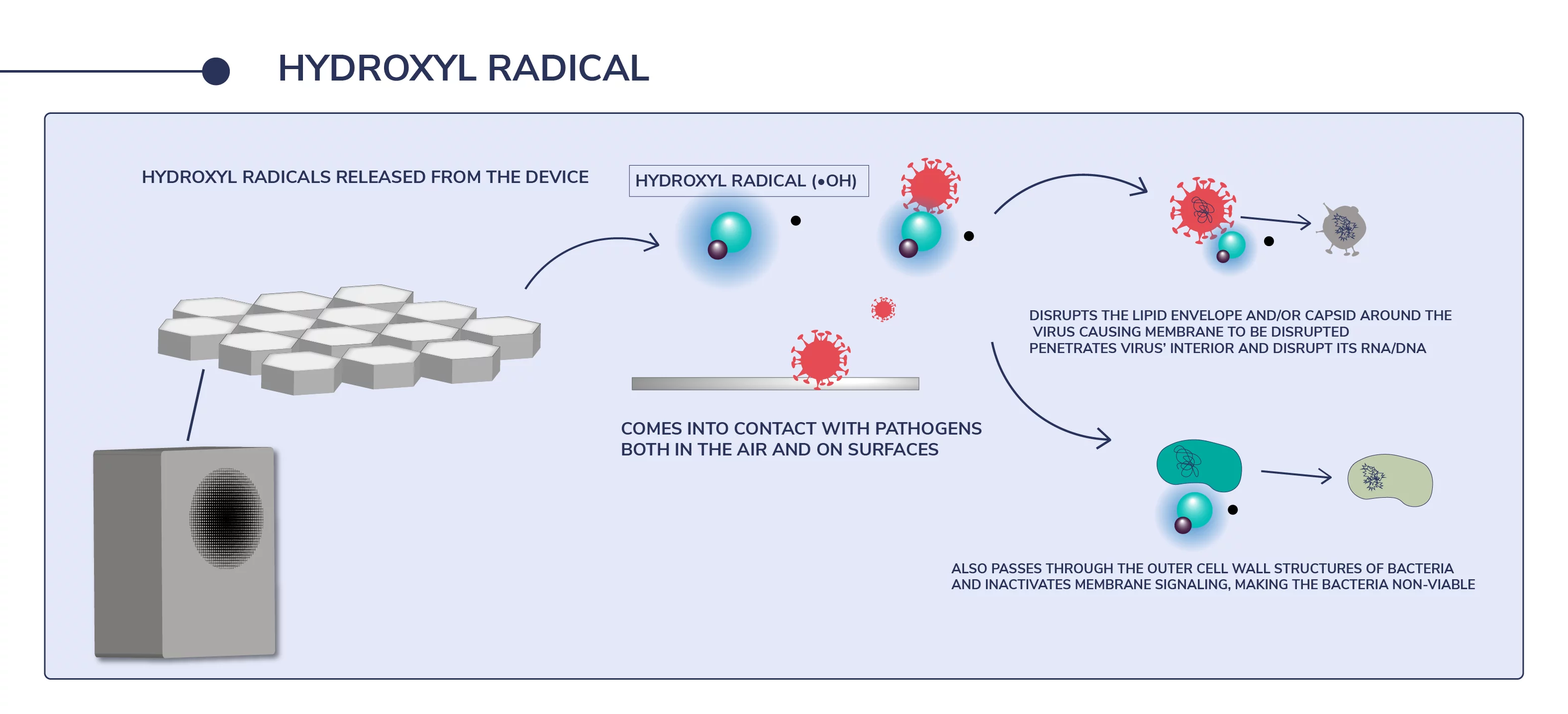
Disrupt the lipid envelope and/or capsid around the virus causing membrane to be disrupted.
Penetrate virus’ interior and disrupt its RNA/DNA.
Pass through the outer cell wall structures of bacteria and inactivate membrane signaling, making the bacteria non-viable.
Deviating from H2O (water) by just one extra oxygen molecule, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a compound composed of two hydrogen and two oxygen molecules. The additional extra oxygen molecule makes hydrogen peroxide an oxidizer – an agent that creates a chemical reaction, in which it accepts electrons from another substance.
Hydrogen peroxide produces destructive hydroxyl free radicals that neutralize membrane lipids, DNA, and other essential cell components within pollutants. This ability to destroy the elements that make up the structure of contaminants means that hydrogen peroxide is considered to have robust germicidal, bactericidal, viricidal, and fungicidal properties.
Trioxygen, also called "activated oxygen", is a natural gas composed of trivalent oxygen, which has the particularity of dissolving without leaving traces or chemical residues, becoming breathable oxygen O2 again in a short period of time.
It is a natural sterilizer with high oxidation power that inactivates or eliminates more than 99.99% of viruses, bacteria, molds, fungi, yeasts, spores, mites ... By breaking down the microbial load in the air and on surfaces.
Trioxygen is a powerful ally in the fight against allergies, asthma and infections.
The trioxygen molecules also attack and neutralize the particles that cause unpleasant odors, leaving a pleasant feeling of clean, regenerated and deodorized air.
Negative ions are used to remove small particles in the air. This can help reduce odors and make the air fresher. Negative ions have also been found to:
inhibit viruses, bacteria, and mold species
decrease stress
regulate sleeping patterns
increase immune function
support mood
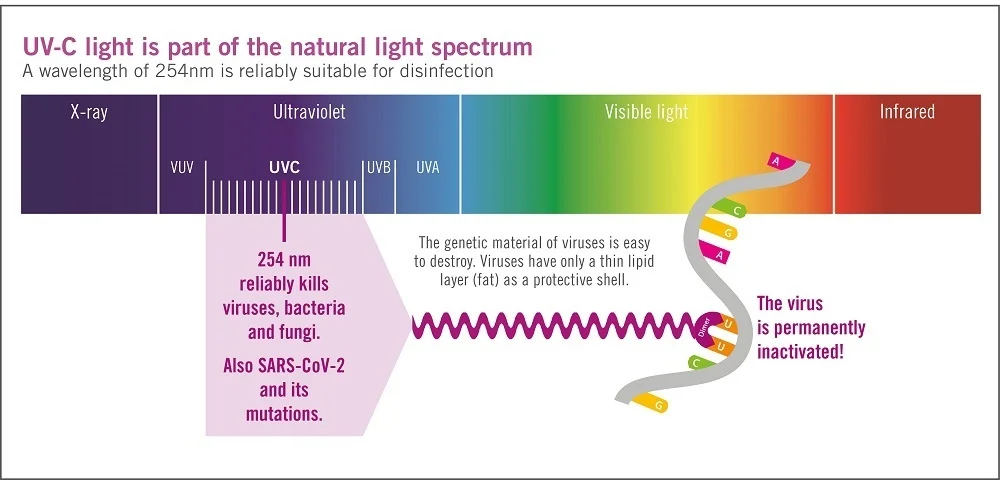
UVC light is used to kill coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2.
Study found that UVC light reduced the live coronavirus by 99.7 percent in 30 seconds.
The type of UVC light used in this study is called far-UVC light, which has the wavelengths of 254 nanometers.
Far-UVC light is damaging to germs but is less of a hazard to human skin and eyes than other types of UVC light.
HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) filter, also known as high-efficiency particulate absorbing filter and high-efficiency particulate arrestance filter. HEPA filters capture pollen, dirt, dust, moisture, bacteria (0.2-2.0 μm), virus (0.02-0.3 μm), and submicron liquid aerosol (0.02-0.5 μm). Some microorganisms, for example, Aspergillus Niger, Penicillium citrinum, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Bacillus subtilis are captured by HEPA filters with photocatalytic oxidation (PCO). A HEPA filter is also able to capture some viruses and bacteria which are ≤0.3 μm. A HEPA filter is also able to capture floor dust which contains bacteroidia, clostridia, and bacilli.
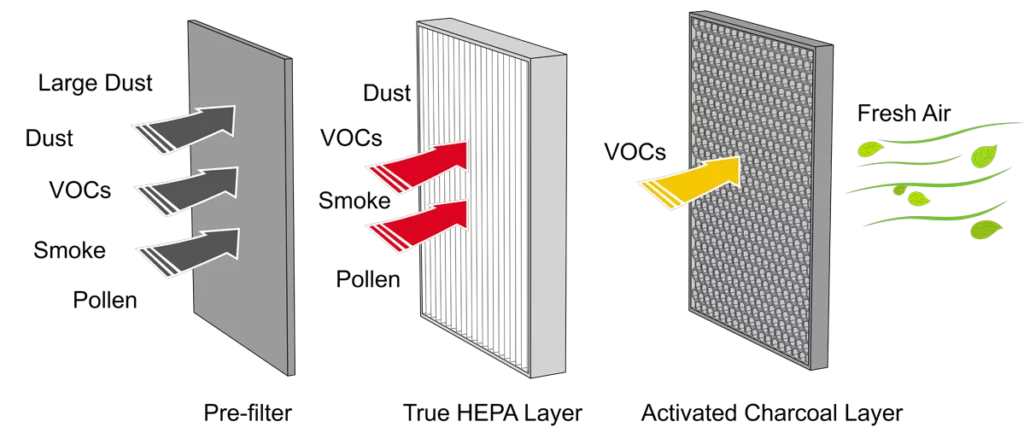
Activated charcoal is charcoal that has been treated with oxygen to open up millions of tiny pores between the carbon atoms. The use of special manufacturing techniques results in highly porous charcoals that have surface areas of up to 2,000 square meters per gram. These so-called active, or activated charcoals are used to adsorb odorous and substances from gases or liquids.