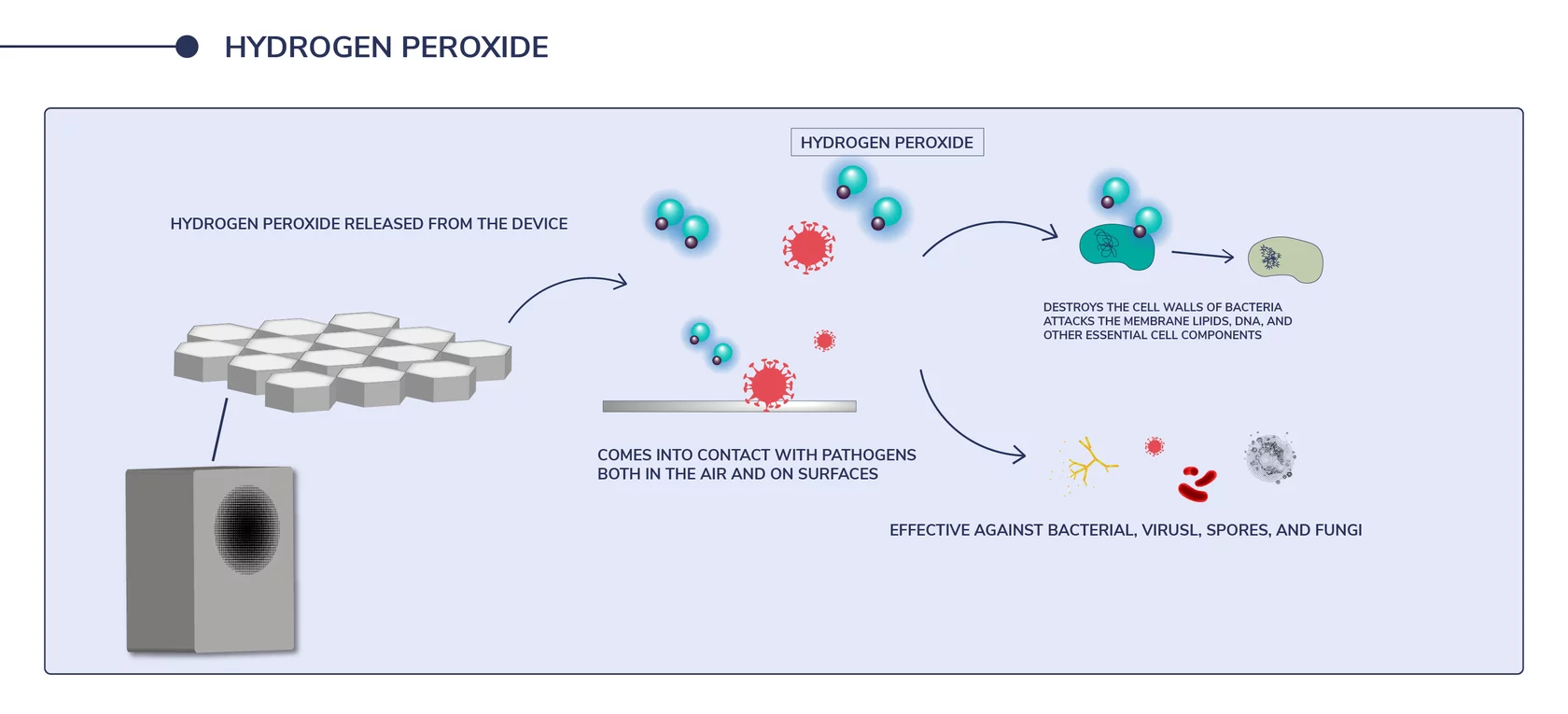
Deviating from H2O (water) by just one extra oxygen molecule, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a compound composed of two hydrogen and two oxygen molecules. The additional extra oxygen molecule makes hydrogen peroxide an oxidizer – an agent that creates a chemical reaction, in which it accepts electrons from another substance.
Hydrogen peroxide produces destructive hydroxyl free radicals that neutralize membrane lipids, DNA, and other essential cell components within pollutants. This ability to destroy the elements that make up the structure of contaminants means that hydrogen peroxide is considered to have robust germicidal, bactericidal, viricidal, and fungicidal properties.